What is Hardware Cloth?
Hardware cloth is a type of woven mesh created by weaving wire of differing dimensions into a flexible metal fabric. It is used for varied purposes like animal cages, fencing, strainers and filtering screens.
Variations in Hardware Cloth is defined by the wire type and gauge, the finish applied and the way the wire fibers at their intersections are knit together.
In hardware cloth, there is an inverse relationship between a higher number gauge and thinner wire produced. The commonly used wires in hardware cloth are 16, 19, 23, 24, 27 where gauge 16 is the thickest and largest.
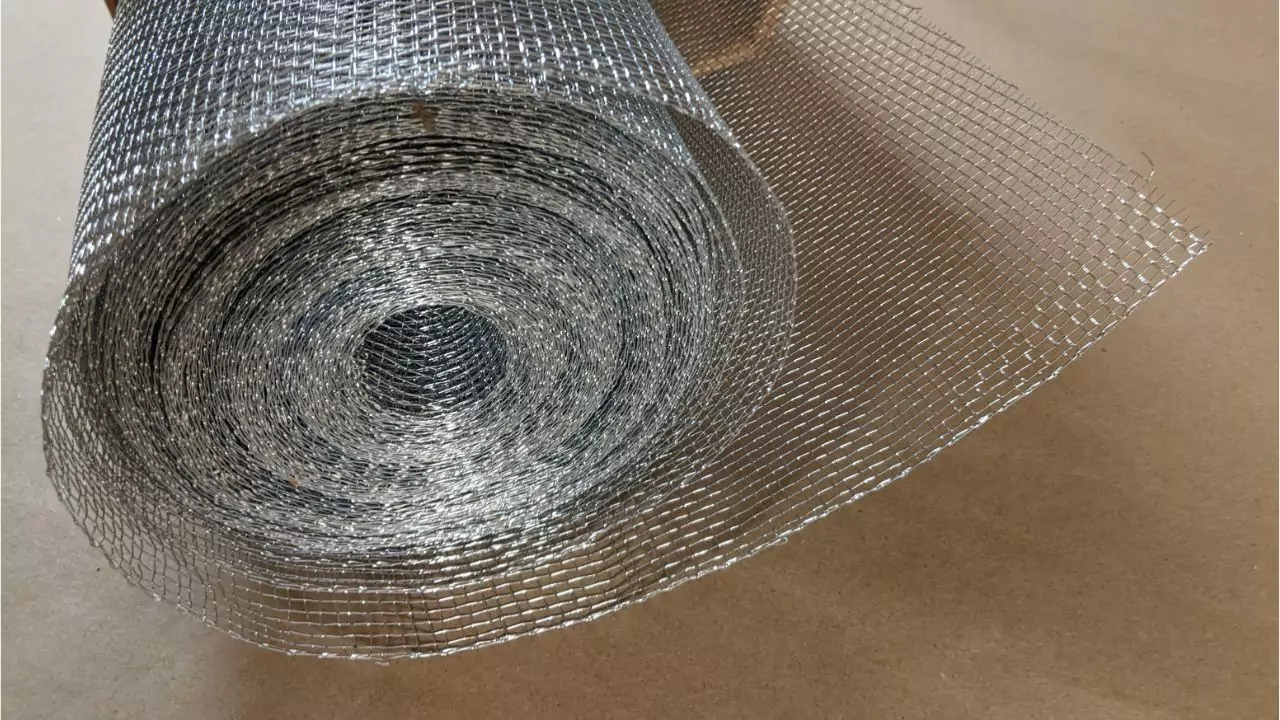
How Hardware Cloth is Made?
Hardware cloth is stitch with parallel rows of wires intersected with columns of wires. It would be reasonable to expect it to be like perforated metals or expanded metal sheets but the way it is made is very different.
It is much more accurate to say that hardware cloth is made using a wire fabricating procedure and may be made from wire of any size, although smaller wire gauges are easier to work with.
A notable difference among various types of hardware cl oth is how the wires are fused together at the intersections. Welding and weaving are the two major techniques employed.
In the welding method, a welding machine that quickly stitches the intersections together is employed to melt intersecting wires to form the necessary joints.
On the other hand, woven hardware cloth is created by interlacing the wires into a fabric using the classical weaving method by employing an over-and-under pattern.
Metals
There are no limitations on the types of metals which can be used to manufacture hardware cloth. However, most manufacturers opt for stainless steel, carbon steel, or galvanized steel.
Historical reasons justify the using of only stainless and galvanized steel for the manufacture of hardware cloth for many years given their immense strength and ability to withstand corrosion.
In the recent past, the incorporation of different varieties of plastic coats on the hardware cloth has increased the possibility of using other kinds of metals.
Stainless steel hardware cloth is manufactured using various grades such as 304, 304L, 316, and 306L and is produced in plain and twill weaves.
Because of the unique properties of carbon steel, it works well for different applications, especially in hardware cloth which needs ductility to facilitate connections that are close together and secure.
The carbon content of carbon steel is used to modify its properties, making it possible to use it for a wide range of applications. For hardware cloth four different types of carbon steel are used based on their specific carbon content.
- Low: Low carbon steel is also referred to as mild steel and contains carbon in the range of 0.05% – 0.25% and manganese up to 0.4%. It is highly ductile and undergoes carburizing in order to improve the surface hardness.
- Medium: Medium carbon steel is known for containing a carbon percentage of 0.29% – 0.54% while its manganese content varies between 0.6% – 1.65%. It is well known for providing high strength and ductility, which helps in providing good wear resistance.
- High: High carbon steel is well known for its strength, hardiness and durability. It has a carbon content of 0.55% – 0.95% and its manganese ranges between 0.3% – 0.9%.
- Very High: Very high carbon steel is known for high strength due to a carbon content of 0.96% – 2.1%, however, this makes the material more brittle and less ductile.
In the past, galvanized steel was the most common material used to make hardware cloth, and it is still very popular today.
But now, metallurgy has developed different materials that can be used for making hardware cloth. Galvanized hardware cloths have a zinc coating to help resist corrosion and increase their durability.
Nearly all metals that can be drawn into wires can be used to make hardware cloths, but commonly used materials for cloths include stainless steel, carbon steel, and galvanized steel.
Welded
To weld hardware cloth fences, the wires are first arranged into rows and columns that are parallel to one another. Wires that will be soldered are preset into the correct shape that matches the required aperture size, before being soldered.
Then, the welding machine makes a number welds on each cross section of the rows and columns that has been made. The machine is supplied with changing wire, and after each row of wire passes through the welding machine, the next row is welded onto the feed wire.
Woven
Woven hardware cloth is made with a number of processes, some of which are known only to certain companies.
While there are several ways to fabricate hardware cloth, the basic method consists of pairing wires together to create an over-and-under pattern just like weaving cloth.
The description given here can serve as the basis for the weaving process, which can be quite difficult owing to methodologies in use.
- Plain Weave: Also referred to as square weave, plain weave is one of the standard methods to make hardware cloth. Here, the warp wires which run parallel to length of the cloth, alternately cross over and under the weft wires which run perpendicular to the cloth. Usually, warp and weft wires are of uniform diameter and gauge.
- Twilled Weave: A twilled weave is characterized by each weft wire alternatively passing over and under every pair of warp wires. This technique is especially useful for heavier gauge wires, for example, 16 or 19, which are too robust for plain weave methods.
- Dutch Weave: The Dutch Weave processes two wires of different gauges, having the warp wire thicker than the weft wire. Oblique weaves are dense due to the tightly packed construction and form hardware cloth with very small openings. Other versions of the Dutch weave are termed as reverse, twilled, and reverse twilled, each having their own attributes and unique qualities on the result product.
- Five Heddle Weave: The five heddle weave is form when fill wire is arranged alternately over and under five warp wires. This method creates parallel oblique lines on the output. The five heddle weave is purposely made to use thicker wires so that it can bear heavy loads.
These four described above are the most popular for manufacturing hardware cloth. Along with these, there is a wide range of other variants, which includes oblong, multilayer, cable, spiral, and some other combination of the mentioned techniques.
Knitted
Knitting with wire produces a hardware cloth with interlacing loops that creates a honeycomb pattern. This process yields a product that is strong, flexible, eco-friendly, has the ability to be compressed, and stretches in both ways.
The machinery employed for wire knitting resembles that used for knitting sweaters and scarfs. Round wires, which are easier to work with compared to flat ones, are the most common for making the hardware cloth.
Crimped
Both ferrous and non-ferrous metals produce crimped wire cloth. Crimped hardware cloth can be produced using different methods such as flat top, lock, double, and intermediate crimping. This type of hardware cloth has square or rectangular openings and is made with different gauge wires thicknesses.
- Flat Top: Flat top crimped, or pressed crimped, hardware cloth is crimped at the top but has knuckles on the back. Both the warp and weft wires are woven after crimping is done to them.
- Lock: Lock crimping uses pre-crimped wires that are bound with bumps or knuckles that hold the crimp guaranteeing that the cloth formed is very rigid. Either side of the raised wire is pressed down to ‘lock’ the wires allowing for no movement.
- Double: Double crimp Hardware cloth uses a weave in which both the warm and the weft wires are locked in by straight wires, which is then secured by crimping it. The crimped sprung formation, as illustrated in the below image, creates a robust and tight weave. The pattern is composed of the warp wires going alternately above and below the fill wires.
- Intermediate: There are two kinds of intermediate hardware crimped cloth – single and double. In a single intermediate crimp, the weft wire is crimped before the warp is woven. In the double type, both the weft and warp wires are crimped prior to the weaving step.
Application of Hardware Cloth
A hardware cloth is a type of a wire product that can be molded in different shapes and sizes for different purposes. It is mostly employed in screen production, as well as part of a filtering and separating system.
Different sizes, styles, types of wire, methods of construction, and mesh configuration of hardware cloth are made for specific purposes, while other cloths have design limitations that are not commonplace and serve uncommon purposes.
The metal type that is utilized is very determinative in regards to how functional and useful the hardware is, or can be, for various applications.
Architectural
Construction hardware cloth is widely used in the field of architecture in order to enhance the beauty of structures. It may help give new buildings a modern, finished look and improve the appearance of old buildings because of its unique texture and structure.
Apart from aesthetics, hardware cloth can also perform basic functions like filtering and shading. It allows for regulation of indoor temperature which, by providing shade, cooling, and heat retention, can result in lower heating bills.
Petrochemical Industry
The hardware cloth used in this sector is fundamental to the filtration and separation of gases and liquids into mist eliminators and demister devices, and so requires rugged, durable, long lasting engineering equipment.
Such cloth can be fabricated from a number of metals including stainless steel, nickel alloys, galvanized steel, carbon steel, and aluminum.
Service life of some metals used for making the hardware cloth will be prolonged by aluminizing the surface which improves performance and service life of the cloth.
Food Processing
Unlike other industries, the food processing industry utilizes lighter metals, such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper for making hardware cloths.
Due to its large open mesh, hardware cloths are highly utilized in sifting flour and other milling processes. Since it comes into contact with food, its use in this industry is subject to Food and Drug Administration (FDA) restrictions.
To facilitate easy cleaning and inhibit the growth of bacteria, plain weave is frequently utilized in the cloths manufacturing process.
Construction
As concrete gradually hardens, it takes on a rigid form, and is usually kept in its desired shape with the use of additional support. Additionally, rebar has been used for this purpose due to its strength and durability.
Its adaptability, ease of ductility, and ease of shaping makes it possible for some people to use the hardware cloth instead lower grade reinforcements for concrete.
Therefore, it is possible for hardware cloth to assist concrete in keeping its shape while also being able to help repair different sized holes on floors and walls.
Enclosures
In the past, chicken wire was often used to enclose plants, animals, and equipment. Chicken wire is useful but can easily be broken or cut.
To solve these problems, gardeners, farmers, and do-it-yourselfers are switching to the use of hardware cloth.
However, its greater density and strength make it more robust in protection by tearing or holding its shape more effectively.
Types Of Hardware Cloth
Based on a crossed wire type, a woven or a welded hardware cloth type, and a covered area type, hardware cloth can be categorized.
These distinctions provide and help identify different forms of hardware cloth. Moreover, its applications serve as a constituent that determines the specific type, as they are made for certain purposes.
From gardening projects to industrial uses, hardware cloth is versatile and used in various fields. Because of its flexibility and adaptability, it has gained wide popularity and usefulness.
Architectural Hardware Cloth
In the context of building engineering and design, aesthetic and hardware cloth have both visual and mechanical requirements.
Their combination offers multiple design choices for architects as well as protection from exterior and interior environmental elements. This type of hardware cloth is meant for provision of architectural design options.
Bolting Hardware Cloth
This type of hardware cloth has the characteristic traits of strength as well as flexibility. It is constructed with thin, smooth, and tough wires that are woven into a screen-like square net which is perfect for both screening and bolting purposes.
Usually made of stainless steel, it has a great resistance to rust and corrosion which makes it suitable for use in sifting and screening materials, further adding to bolting hardware’s durability.
Filtering Hardware Cloth
This type of cloth is designed specially for bolting and filtering purposes due to their durability and strength which comes with robust warp wires. The design makes it ideal for separation of slurries and liquids.
This cloth has an array of weaves including but not limited to: plain Dutch, twilled Dutch, and reverse Dutch which give it greater porosity and ease of cleaning. It is often selected over the use of synthetic or fiber filters due to its superior filtering performance.
Galvanized Hardware Cloth
The fabrication of galvanized hardware cloth incorporates the use of zinc, in a hot-dip galvanizing process. The resulting coating serves an outer barrier that makes the product suitable for outdoor applications.
Light gauge wire is used in the creation of galvanized hardware cloth, which finds application for fencing, construction, and even pest control.
Galvanized hardware cloth has numerous unique features including waterproof, durable, rust-resistant, long-lasting, and lightweight. Its featherweight characteristic does not compromise the strength, stability, and endurance offered by the galvanized hardware cloth.
Market Grade Hardware Cloth
Market grade hardware cloth is a type of woven wire in standard cross section dimensions and wire combinations. Its manufacture uses several metals and it is usually sold in hardware and improvement shops with variable openings per linear inch.
Market grade hardware cloth is made of heavier wires (such as 16 and 19 gauge) and therefore is intended for use in heavy-duty applications.
Mill Grade Hardware Cloth
Mill grade hardware cloth is marketed as the lightweight version of market grade cloth. It is manufactured using stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
Mill grade hardware cloth also features lower wire diameters compared to market grade (for example 23 or 27 gauge). Although it has fewer openings, this grade is ideal for sifting and milling flour as well as light material processing.
Refinery Grade Hardware Cloth
Refinery grade hardware cloth is utilized in a petroleum refinery and gas plants. As it is industrial grade, it is either woven or welded to very strict reliability and endurance standards.
It is used in pipe fittings as well as in grids supporting catalysts. These have continuous slots in them so that pullings and clogging do not happen. Another important thing is that they are robust.
Space Hardware Cloth
Space hardware cloth is produced by using weaving and welding processes. The name comes from the distance in between the wire strands as it was designed to be during construction.
Space hardware cloth is commonly used as a screening material for gravel sand, powerful tools and aggregates. These accurately size, wash, classify, and separate materials, space hardware cloths aid in doing so.
What metals are commonly used to make hardware cloth?
Any metal that can be formed into wire is capable of forming into hardware cloth. Years of making wire cloth, wire mesh, and chicken wire stainless, carbon, and galvanized steel were the three mostly used.
With modern production methods and techniques, other metals have been incorporated into the production of hardware cloth.
The selection of metal for hardware cloth is primarily based on its purpose. Stainless steel, carbon steel and galvanized steel have always been preferred for a long time due to their strong and durable nature and flexibility.
Nevertheless, such favorable traits are available in other metals that can be picked depending on the users’ needs and circumstances.
Aluminum
With the invention of effective processes for purifying aluminum, this metal is the most utilized in the market.
As the lightest available metal, aluminum is 35% lighter than steel and possesses remarkable ductility making it beneficial in creating hardware cloth.
Aluminum is preferred when there is need of a lightweight metal. It is seldom used in pure form as most of the time, it is part of an alloy with other stronger metals to increase its tensile strength and utilize its corrosion prevention properties.
Nickel
Nickel is used in alloys, as its combination with other metals do improve their characteristics. It can be oxidized and corroded, although it does not lose its strength in elevated temperatures nor does it succumb to chemical and acidic conditions.
Nickel alloys are commonly used in constructing filters, separators and strainers in petrochemical, pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
Bronze
An alloy of copper, bronze retains all the attributes of copper, which include its malleability, durability, and ductility. The bronze used to manufacture hardware cloth contains 90% copper and 10% zinc.
Bronze wire hardware cloth is employed in areas subject to atmospheric corrosion, particularly in marine environments. Just like nickel, bronze is also frequently used as material for filters and separators. Due to its aesthetic features, bronze finds application in architecture.
Brass
Brass is a mix of copper and zinc with 65% and 35% content respectively. This is a very soft metal which can be shaped into different forms and molded easily, but has low durability.
As with bronze, the high zinc content gives brass resistance against abrasives and enhances its tensile strength, thus making it more durable than bronze.
Similar to bronze, the aesthetic appeal of brass attracts the attention of designers and architects, making it a preferred material for detailing construction masterpieces. Brass has industrial applications in manufacturing of filters and separators.
Titanium
Titanium is a silver-white substance known as an exceptionally strong and corrosion-resistant metal with great biocompatibility and shape memory qualities.
Titanium also has great application in the construction of seawater filtration, water purification, and chemical drug filter, for which Hardware cloth made from titanium are used.
Offering a strength-to-weight ratio superior to steel by 60%, titanium has a density well within the range of this other metal.