What is Wire EDM (electrical discharge machining)?
Wire EDM is also known as: wire-cut EDM, EDN cutting, EDM wire cutting, and ‘cheese-cutter’ EDM.
Wire electrical discharge machining is a non-contact subtractive manufacturing process that uses an electrically charged thin wire with a dielectric fluid to cut a metal part into different shapes.
The process produces small chips and precise cut lines by melting or vaporizing the material rather than cutting it. As a result, it can conveniently machine parts unsuitable for conventional machining techniques. However, the parts must be electrically conductive.
Wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) uses a metallic wire to cut or shape a workpiece, often a conductive material, with a thin electrode wire that follows a precisely programmed path.
Typically, the electrode diameters range from .004″ – .012″ (.10mm – .30mm), although smaller and larger diameters are available.
During the wire cutting process there is no direct contact between the wire and the workpiece which allows for machining without causing any distortion in the path of the wire, or the shape of the material.
To accomplish this, the wire is very rapidly charged to a desired voltage. The wire is also surrounded by deionized water.
When the voltage reaches the correct level, a spark jumps the gap and melts a small portion of the work piece. The deionized water cools and flushes away the small particles from the gap.
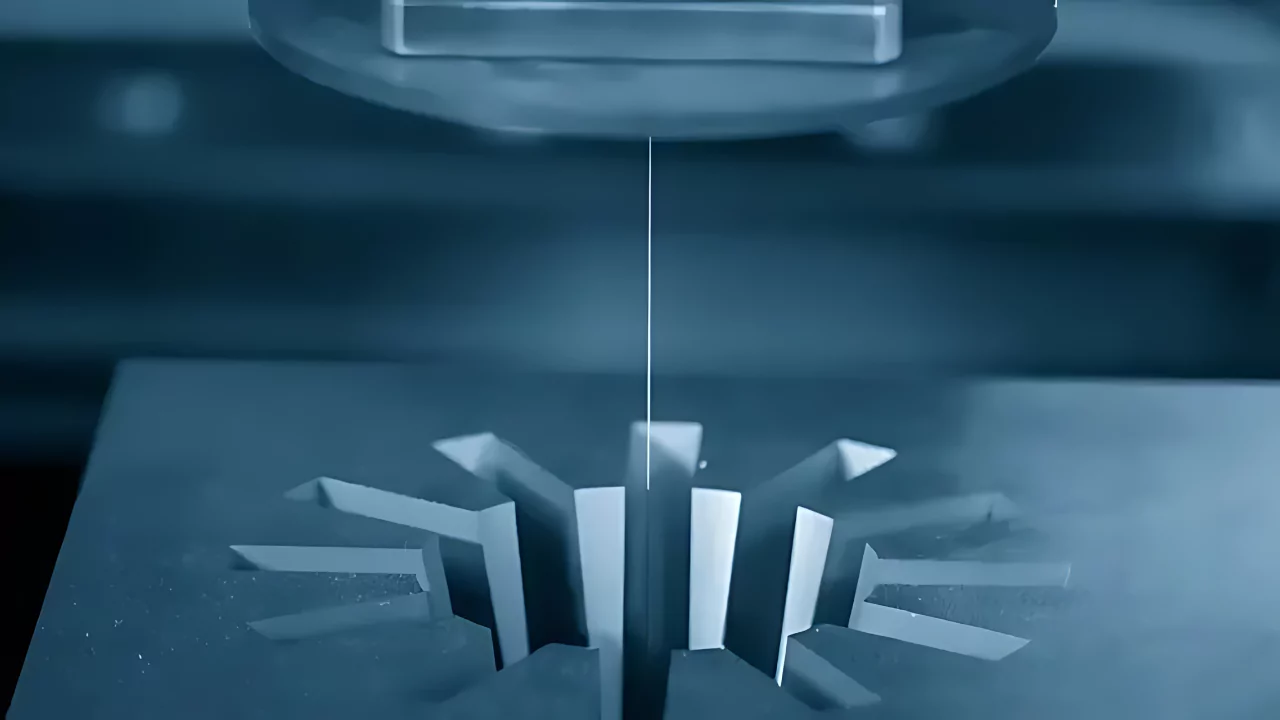
How Does Wire EDM Work?
The wire-cut EDM process has a simple mechanism.
Machining a part using the process involves submerging the workpiece into a dielectric fluid, securing it with a machinist vise, and running the wire through it to produce sparks as it passes an electric current.
In other words, the wire carries one side of the charge, and the workpiece, which must be a conductive material, carries the other side of the charge.
When the two get close, a hot electric charge jumps the gap and melts tiny pieces of the metal away.
The electric spark is the cutting tool to cut the material in the desired shape. Additionally, the wire EDM process involves deionized water to control the process and flush away tiny particles removed.
During the wire EDM process, the material is carved, shaved, and otherwise removed from the workpiece through a series of repetitive current discharges between a wire electrode and the conductive substrate.
The electrode and workpiece are immersed in a dielectric fluid, such as deionized water, maintaining a gap between them.
Wire EDM uses potential difference, which is applied to the electrode and workpiece in pulse form.
As this occurs, electrons from the negative electrode move towards the positive workpiece, colliding with the molecules of the deionized water.
The electrons convert the molecules into ions, increasing the concentration of ions and electrons between the electrode and workpiece. The electrons move towards the electrode and the ions move towards the workpiece, which creates an electric current.
As the electric current moves between the electrode and workpiece, the temperature increases to approximately 10,000° C.
The intense heat vaporizes and melts material away from the workpiece. Once the current stops, the molten material is carried or flushed away by circulating dielectric fluid.
The accuracy of the wire EDM process is heavily dependent on cutting parameters and speed. At higher speeds, the wire can slightly move or bend, affecting overall accuracy.
To ensure the highest possible accuracy, it is best to maintain lower power and speed. With higher speeds, tolerances of +/- 0.001’’ are achievable, while tolerances of up to +/- 0.0002’’ are achievable with lower power and speed.
When compared to other methods of machining, such as CNC machining, milling/turning, and laser drilling, wire EDM offers a wide range of advantages.
Although these alternative techniques offer certain benefits for specific applications, they also have numerous disadvantages.
Parts of A Wire EDM Machine
The components of a wire EDM machine collaborate to precisely shape materials. Each part plays a crucial role, and their coordinated function is essential for the machine’s operation.
#1. Electrodes.
In wire EDM, the wire functions as the cathode, while the workpiece acts as the anode in the machine’s electrode setup. During the cutting process, the servo motor regulates the wire electrode to prevent it from touching the workpiece.
#2. System for Running Wire.
The wire feed system manages the electrode wire’s speed and tension, controls its back-and-forth movement, and ensures that the wire coils onto the drum properly without overlapping.
#3. Working Table.
The workpiece is secured on the work table, which is moved by two stepper motors. The interaction between the moving table and the cathode wire enables the wire EDM process.
The high-speed wire feed EDM machine features X and Y axis slides on its work table, utilizing advanced linear guideways and ball screws for movement.
The XY cross structure, a time-tested design, provides robust mechanical rigidity and precision control. This design is now well-established and commonly employed in the manufacturing of various machine tools.
#4. CNC Control.
CNC systems rely on high-precision stepper motors that feature robust coupling and programming capabilities. These systems are crucial for managing the complete wire EDM machining process.
They automate the cutting operation and manage the sequencing of the wire path to ensure accurate results.
#5. Dielectric Fluid.
The tank for the wire-cut EDM process must be filled with dielectric fluid. This fluid prevents tiny particles from sticking to the wire electrode during machining.
Deionized water is commonly used because it cools the operation and helps achieve a smooth surface finish on the workpiece.
#6. Power Supply.
The power supply unit sends pulses between 100V and 300V to the wire electrode and the workpiece. The electrical charges that flow through the wire electrode to interact with the workpiece are also controlled in frequency and intensity.
Therefore, a highly-developed power supply unit is required to deliver the right kind and quality charges during wire EDM machining.
#7. Recycling System.
Deionized water is pumped from the tank, filtered to eliminate impurities, and then channelled through separate nozzles before returning to the tank via another filter.
If the quality of the working solution or the effectiveness of the filter affects the cutting process, they should be replaced.
#8. Wire
The wire serves as the electrode to create the electrical discharge. The shape and thickness of the workpiece directly influence the wire’s diameter.
Typically, one can use wires with diameters ranging from 0.05 to 0.25mm. The main types of wires used include
Brass Wires
Brass is the most common EDM wire material because of its excellent conductive properties. It is an alloy of copper and zinc, and the higher the zinc content, the faster the wire cuts.
However, there should be a balance because when the zinc content is over 40%, this decreases the corrosion rate of the brass wire.
Zinc coated Wires
As the name implies, you obtain it by applying a coating of pure zinc or zinc oxide on the wire surface. Manufacturers use zinc-coated wires because it improves the machining speed.
Diffusion-annealed Wires
The diffusion annealing process helps to create wires with higher zinc content (more than 40% zinc). It involves coating wires with layers of pure zinc. These wires are ideal for mass production and can machine many materials.
How to Choose the Right Wire
- To choose the right EDM wire material for your project, consider the following
- Tensile Strength
- Fracture Resistance
- Conductivity
- Vaporization Temperature
- Hardness
Materials A Wire EDM Machine Can Cut
Any conductive material such as steel, titanium, aluminium, brass, alloys and superalloys can be cut using the EDM wire method.
With its accuracy, the EDM wire cut technique has become a convention cutting method in all industries. Machine parts, logos and other metals can be cut and made with ease using EDM wire.
The use of EDM wire for producing parts or its prototype depends on the thickness and size of the part to be cut and the length of cut to be created.
If you are looking for assistance while buying a wire-cut EDM machine, reach out to us today. Our dedicated team of experts can guide you to find the best machines per your requirements and goal.
Many metal materials are difficult or impossible to machine without adding heat; with wire cut EDM hole drilling, these materials can be worked with exceptional precision without applying heat.
Wire cut EDM hole drilling is fast, effective, and can be used to machine virtually any electrically conductive or heat-treated metal material, including:
- Bronze
- Copper
- Tungsten
- Carbon graphite
- Carbon steel
- High alloy steel
- Inconel
- Stainless steel
- Hastalloy
- Titanium
- Kovar
What is Wire EDM Accuracy?
Speed and precision are controlled by managing cutting parameters power and frequency and controlling the rate of fluid flushing.
Lower power and speed improve accuracy. This is because flushing moves the wire slightly, and flushing pressure is higher at higher feed rates.
In addition, the wire bends slightly in a phenomenon known as barreling and at higher speeds the effect is more pronounced.
Tolerances of +/- 0.001” are achievable during a relatively quick roughing pass. Cutting the power and reducing flushing pressure for a skim achieves around +/- 0.0005”. Following up with a second skimming pass improves the precision of EDM, to around +/- 0.0002”.
Differences Between EDM Wire Cutting and Conventional EDM
The wire-cut EDM process is an improvement on conventional EDM. Their mode of operation is similar.
Sinker EDM uses electrodes, while Wire EDM uses a thin wire as the cutting tool.
The sinker EDM process is better suited for more complex shapes and geometries, whereas wire EDM is ideal for producing components with strict tolerance requirements and ultra-high precision.
However, they have significant differences. Below are a few differences between both machining process.
1. Electrode.
As stated above, the electrode used in wire EDM cutting is a thin heated wire. In contrast, conventional EDM uses highly conductive metals like graphite or copper electrodes to produce electrical charges.
The electrodes are in different shapes and sizes, which affects their smoothness. For example, a round electrode produces the smoothest surface.
Then a square, triangle, and diamond. When the electrode is inserted into the workpiece, it forms a mold leaving a ‘negative’ impression of its shape.
2. Speed of Machining.
The electrodes of conventional EDM must come in different shapes. As a result, manufacturers must create and shape them before the machining process, and this takes time.
In contrast, the wire EDM machine is ready to use as soon as the wire is in position. This makes it appropriate for applications that must need to be completed quickly.
3. Accuracy.
Wire EDM machining makes use of wire as the electrode. As a result, they have better accuracy than conventional EDM.
For example, the wire electrode allows them to cut at a thickness of about 0.004inches. Due to their accuracy, they become better suited for machining parts with complex shapes and designs, unlike the conventional EDM, which is more suitable for more rigid cuts.
4. Applications.
Wire EDM machining is versatile and can cut ferrous and non-ferrous metals, so many industries use it. Also, size and shape do not limit its use because it can machine both long parts and extremely small ones.
However, conventional EDM can handle harder and thicker materials because the thickness of the wire electrode in a wire EDM machine affects its use.
Pros and Cons of Wire EDM Machining
Pros of Wire EDM
- It makes precise and accurate cuts eliminating the need for further processing and finishing of the workpiece.
- The process is suitable for creating complex designs and shapes that are otherwise challenging to produce using traditional CNC machining.
- It is applicable in machining small parts and for cutting highly detailed items that would otherwise be too delicate for other machining options.
- Wire EDM machining is ideal for fragile materials and cannot withstand the stress of machining.
- With just one stage of processing, the machine cuts materials leaving no burrs or distortion.
- The machining process cuts continuously without interruptions. Even if the wire breaks when cutting, the process continues immediately.
Cons of Wire EDM
- It is only compatible with materials that conduct electricity.
- An oxide layer may develop on the cut surface of some materials, such as aluminum. Therefore, this could necessitate additional finishing, which raises the cost.
- It has a high initial investment and maintenance cost.
Applications of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining
Wire EDM is most commonly used in mold and die manufacturing processes, particularly for extrusion dies and blanking punches.
EDM can be used in everything from prototypes to full production runs, and is most often used to manufacture metal components and tools.
Many industries use wire EDM machines from prototyping to complete production runs. Below are some industries.
Automotive Industry
The parts in the automotive industry come in complex shapes and sizes and are mostly hard. As a result, the industry favors using wire EDM machines because the process does not rely on mechanical forces, and the wire electrode does not need to be stronger than the workpiece.
The process applies to making holes and cavities to customize automotive car parts like bumpers, dashboards, car doors, and many more.
Medical Industry
Wire EDM machines produce complex parts with a high level of accuracy for use in all medical fields, including optometry and dentistry.
Also, metals that work well with wire EDM services are frequently used to manufacture medical equipment.
Since the wire’s diameter determines the cut’s size, the wire EDM machine adds tiny features to parts like dental implants and syringe components without endangering their structural integrity.
Aerospace Industry
Wire EDM cutting produces parts with tight tolerances and is the go-to machining process for aerospace part manufacturers.
This process, alongside the waterjet cutting process, is especially used for parts that cannot withstand the high temperature and stress associated with traditional cutting tools.
Parts in the aerospace industry need to have an excellent surface finish and be precise and accurate. Manufacturers use the wire EDM process for years to make engines, turbine blades, landing gear parts, and many more.